Contents
- 1 Basic
- 1.1 Find a file
- 1.2 Script to add to .bash_profile to load .bashrc
- 1.3 Clean output when running a command that may throw errors
- 1.4 Don’t get either output or errors
- 1.5 List files ordered by last modification time
- 1.6 Create a folder and sub-folders and not fail if it already exists
- 1.7 Automate actions to do on folders or sub-folders with Bash
- 1.8 Get the logs from a specific date
- 1.9 Run a command on a host
- 1.10 Find a command used recently
- 1.11 Start, stop or restart services, or get their status
- 1.12 Delete files except the most recent ones
- 1.13 Copy files from one host to another
- 1.14 Generate a random password
- 1.15 Decode text in base64
- 1.16 Encode text in base64
- 1.17 Create aliases receiving input params
- 1.18 Main folders in Unix
- 2 User and group management
- 3 Networking
- 3.1 Find the service running on a port:
- 3.2 Open a port on a Unix box server to check connectivity from outside
- 3.3 Connect from local to a website using SSH tunneling
- 3.4 Test the download speed of the internet connection
- 3.5 Prevent SSL_ERROR_SYSCALL when doing connectivity tests
- 3.6 Test connectivity without proxy
- 3.7 Test connectivity via proxy with telnet
- 3.8 Test connectivity via proxy without telnet
- 4 Disk and memory checks
- 4.1 Check disk space
- 4.2 See space available in a location
- 4.3 See where a volume is mounted
- 4.4 See processes using most memory
- 4.5 See the network interfaces configured in a host
- 4.6 See the network interfaces in which a port is running
- 4.7 See the routes configured in a host
- 4.8 File compression
- 4.9 Compress files with password
- 4.10 Uncompress 7z files
- 4.11 Uncompress tar files
- 4.12 Compress files with tar
- 4.13 Uncompress gzip files
- 5 Cron schedulers
- 6 Other schedulers
Basic
Find a file
find / -name *REPLACE_NAME_PART* -type f
Script to add to .bash_profile to load .bashrc
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then . ~/.bashrc fi
Clean output when running a command that may throw errors
REPLACE_COMMAND 2> /dev/null
Don’t get either output or errors
It will send errors to standard output, and output to null:
REPLACE_COMMAND > /dev/null 2>&1
Another way, redirecting both output and error to null:
REPLACE_COMMAND &> /dev/null
List files ordered by last modification time
ls -ltr
Create a folder and sub-folders and not fail if it already exists
mkdir -p REPLACE/FOLDER/PATH
Automate actions to do on folders or sub-folders with Bash
for folder in *;do echo ${folder};cd ${folder};ADD_OTHER_ACTIONS;cd ../;done;
Get the logs from a specific date
Useful if we don’t have access to them in Kibana
ls -l --time-style="+%Y-%m-%d" libs | grep '2022-08'
Run a command on a host
ssh REPLACE_HOST 'REPLACE_COMMAND_TO_RUN'
Find a command used recently
history | grep REPLACE_COMMAND_TO_SEARCH
Start, stop or restart services, or get their status
/usr/bin/systemctl REPLACE_OPERATION REPLACE_SERVICE_NAME
Delete files except the most recent ones
find ${REPLACE_FILE_PATTERN} -mtime +${REPLACE_DATES_TO_KEEP} -delete"
Copy files from one host to another
rsync -avh SOURCE_PATH DESTINATION_PATH
Generate a random password
openssl rand -base64 32
Decode text in base64
echo REPLACE_TEXT | base64 --decode
Encode text in base64
echo -n REPLACE_TEXT | base64
Create aliases receiving input params
We can use functions for them. We can add them to a script that is loaded from .bashrc using
". REPLACE_SCRIPT_PATH"
REPLACE_FUNCTION_NAME () {
# Do any desired action using $1... for the input params
}
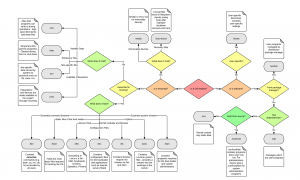
Main folders in Unix
A great diagram a colleague shared with me a while back. I hope I will find who created it to say thanks and give them the credit they deserve for it ![]()
User and group management
Group limitation
Unix systems (using NFS) only allow membership to 16 groups. Users with access to more than that may experience problems accessing files for some groups
Find the groups the current user has access to
id -a groups
Networking
Find the service running on a port:
Multiple ways:
- lsof -i :REPLACE_PORT
- fuser REPLACE_PORT/tcp
- ps -ef | grep REPLACE_PORT
- netstat -nat | grep LISTEN | grep REPLACE_PORT
Open a port on a Unix box server to check connectivity from outside
nc -kv4 -l REPLACE_PORT > REPLACE_LOG_FILE_PATH 2>&1 &
The last part is to get logs from both normal and error outputs
Connect from local to a website using SSH tunneling
When the box where it runs is not directly accessible and we have to access it through another server:
ssh -L LOCAL_PORT:HOST:REMOTE_PORT -N -f USER_ID@HOST
On the web browser open localhost referencing that port, for example:
https://localhost:LOCAL_PORT
Test the download speed of the internet connection
Download a big file and see its file and the download time. Not accurate but gives an idea.
wget -O /dev/null REPLACE_BIG_FILE_LINK
Prevent SSL_ERROR_SYSCALL when doing connectivity tests
export NO_PROXY=BASE_DNS_DESTINATION_ENDPOINT
Test connectivity without proxy
Different ways:
- curl REPLACE_DESTINATION_HOST REPLACE_DESTINATION_PORT
- telnet REPLACE_DESTINATION_HOST REPLACE_DESTINATION_PORT
- nc -vz REPLACE_DESTINATION_IP_ADDRESS REPLACE_DESTINATION_PORT
Test connectivity via proxy with telnet
Connect to the proxy via telnet:
telnet REPLACE_PROXY_DNS REPLACE_PROXY_PORT
And once connected run this to check the proxy can connect to the destination:
CONNECT REPLACE_DESTINATION_HOST:REPLACE_DESTINATION_PORT
Test connectivity via proxy without telnet
export http_proxy=REPLACE_PROXY_DNS:REPLACE_PROXY_PORT export https_proxy=REPLACE_PROXY_DNS:REPLACE_PROXY_PORT curl REPLACE_DESTINATION_HOST:REPLACE_DESTINATION_PORT
Disk and memory checks
Check disk space
See the space available on the main folders:
df -kh
See the space used by the folders under the current folder:
du -skh *
See space available in a location
df -H REPLACE_LOCATION_PATH
See where a volume is mounted
df -kh .
See processes using most memory
- ps aux –sort=-%mem | head
- ps -o pid,user,%mem,command ax | sort -b -k3 -r
See the network interfaces configured in a host
ip link show
See the network interfaces in which a port is running
netstat -tnl | grep REPLACE_PORT
See the routes configured in a host
route -n
File compression
Compress files with password
zip -e files.zip files_to_add
Uncompress 7z files
7za x myfiles.7z
Uncompress tar files
tar -zxvf REPLACE_TAR_FILE_NAME -C REPLACE_DESTINATION_PATH
Compress files with tar
Always use local relative path instead of absolute ones with tar. Tar puts the files together, gzip compresses then:
- tar -cvzf REPLACE_TAR_FILE_NAME REPLACE_FOLDER_TO_COMPRESS
- gzip REPLACE_TAR_FILE_PATH
Uncompress gzip files
gzip -d REPLACE_FILE_PATH
Cron schedulers
They all require systemd or systemctl:
- cron
- cronie
- anacron
Other schedulers
- watch: it doesn’t seem to work inside a script
- Use an external scheduler such as Control-m
- Use a “while true” combined with sleep in Bash script if the other options are not available